Bathymetry
Keel Scar 2 (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds
Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data show ocean floor gouges caused by icebergs moving away from the Antarctic continental ice mass. At this location, these icebergs have probably broken off the Ross Ice Shelf. Areas without multi-beam data are darkened.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: Antarctic
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Expedition:
Chief Scientist:
Species:
Keel Scar 1 (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds
Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data show ocean floor gouges caused by icebergs moving away from the Antarctic continental ice mass. Areas without multi-beam data are darkened. Inset shows geographic location.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: Antarctic
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Expedition:
Chief Scientist:
Species:
Ice Gouge 3 (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds
Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data show ocean floor gouges caused by icebergs breaking off the Antarctic continental ice mass. Areas without multi-beam data are darkened. Inset shows geographic location.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: Antarctic
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Expedition:
Chief Scientist:
Species:
Ice Gouge 2 (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds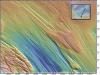
The plowing action of moving ice masses cuts linear depressions, or ice gouges, into the seafloor sediments and bedrock near Antarctica. Inset shows geographic location.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: Antarctic
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Expedition:
Chief Scientist:
Species:
Ice Gouge 1 (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds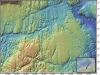
The plowing action of moving ice masses cuts linear depressions, or ice gouges, into the seafloor sediments and bedrock near Antarctica. Inset shows geographic location.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: Antarctic
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Expedition:
Chief Scientist:
Species:
Nantucket Sound (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds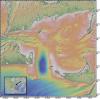
This view shows the southern side of Cape Cod, from Woods Hole on the left to Chatham on the right. The islands of Martha's Vineyard (left) and Nantucket (right) are separated by the deep water (blue) of the Muskeget channel. Shifting sandbars show up clearly in this image. An offshore wind farm of wind-driven electricity-producing windmills has been proposed for Horseshoe Shoals, the shallow (brown-white) area north of the Muskeget channel.
Mississippi (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 17:43 — mgds
The Mississippi River, the largest river in North America, loses velocity and divides into 'distributaries' as it meets the Gulf of Mexico. Sediment from much of central North America is deposited in an expanding fan-shaped delta. The accumulation of sediment is ever-changing, and the Mississippi's primary channel shifts frequently in the delta region. The surrounding areas consist of coastal mudflats, marshes, and tidal pools.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: North America
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Bay of Bengal (2008)
Fri, 07/11/2008 - 11:51 — mgds
This image shows the Bay of Bengal, the Indian subcontinent to the west and Indochina to the east. In the black and white image, the boundary between land and sea is blurred, emphasizing the roughness of the Himalaya mountains in the north and the undersea topography in the Andaman Sea near Indochina. It was along this plate boundary, near the tip of the island of Sumatra, that the December 26, 2005 earthquake ocurred, causing a major tsunami and loss of human life.
Kilauea (2008)
Thu, 07/10/2008 - 15:31 — mgds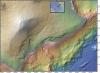
The smooth slopes of this volcano indicate that it is a shield volcano, producing large flows of lava. The Hawaiian Islands were formed by volcanoes of this type. Kilauea is the most historically active of Hawaii's volcanoes; it is currently erupting.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: Hawaii
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry
Device Type: Sonar:Multibeam
Feature:
Investigator: MGDS
Expedition:
Chief Scientist:
Species:
Red Sea and Gulf of Suez (2008)
Mon, 07/07/2008 - 15:27 — mgds
The Red Sea/Gulf of Suez region is a MARGINS ancillary focus site for the Rupturing Continental Lithosphere initiative. The goals of the initiative are to develop a clearer understanding of the physics by which the continental lithosphere deforms, the manner in which strain is partitioned, either spatially or temporally, and the timing, composition, spatial distribution and melting depth of rift-related magmas.
Species (common):
Year: 2008
Details: MARGINS Focus Site
Media Type: Map
Data Type: Bathymetry

